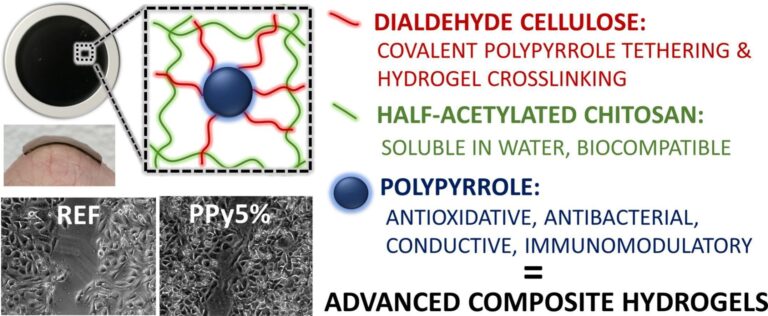
New publication: Chitosan/dialdehyde cellulose hydrogels with covalently anchored polypyrrole: Novel conductive, antibacterial, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory materials
Our colleague Doctor Ondřej Vašíček has published a new paper in cooperation with Doctor Jan Vícha and Professor Petr Humpolíček from Tomáš Baťa University in Zlín.
In this work, conductive composite hydrogels with covalently attached polypyrrole (PPy) nanoparticles were prepared. These hydrogels are based on partially re-acetylated chitosan, which is soluble at physiological pH, simplifying synthesis and purification. Low-toxic dialdehyde cellulose (DAC) was used for crosslinking chitosan and anchoring PPy particles. This is the first report of the condensation reaction between DAC and PPy, which improves PPy anchoring and control over the composite’s properties. The combination of chitosan and PPy enhances the biological properties of the hydrogels, making them non-cytotoxic, non-irritating, antibacterial, and capable of capturing reactive oxygen species. They also have conductivity similar to human tissues, promote in vitro cell growth, and have immunomodulatory effects. The covalent attachment of PPy strengthens the hydrogel network, presenting a promising method for developing advanced biomaterials.