New publication: Factors influencing the efficacy of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator: Implications for ischemic stroke treatment
Dr. Jan Víteček’s group, based in our department, has published a new paper focused on ischemic stroke. The publication was produced in collaboration with Professor Robert Mikulík’s team from St. Anne’s University Hospital in Brno.
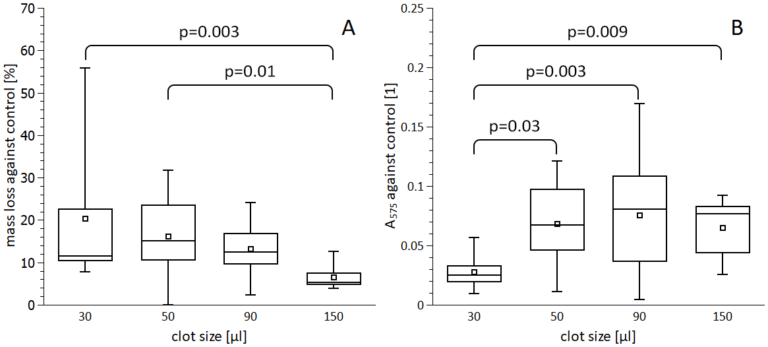
This publication investigates factors that limit the efficacy of intravenous thrombolysis using recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA) in treating acute ischemic stroke. The study aims to understand the impact of clot size, rt-PA concentration, clot age, and the combination of rt-PA with heparin on the thrombolysis process. Using an in vitro model with red blood cell-dominant clots from healthy donors, the study found that clots larger than 50 μl are challenging to degrade at a clinically relevant rt-PA concentration of 1.3 mg/l. Changes in rt-PA concentration only slightly affected clot degradation, and heparin had no impact on rt-PA-induced thrombolysis. Younger clots were more susceptible to thrombolysis, suggesting that prompt rt-PA treatment after stroke onset could improve outcomes.